
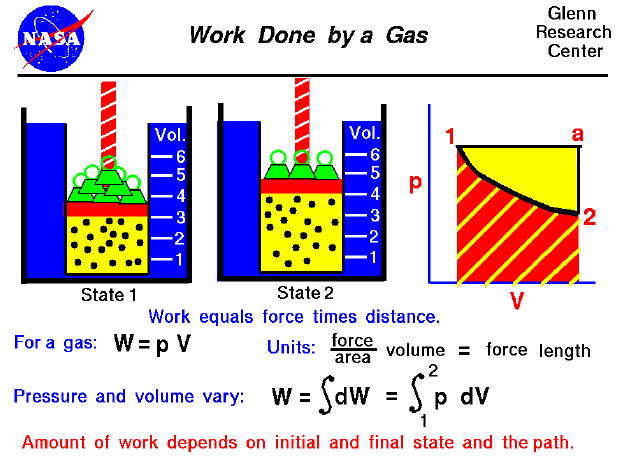
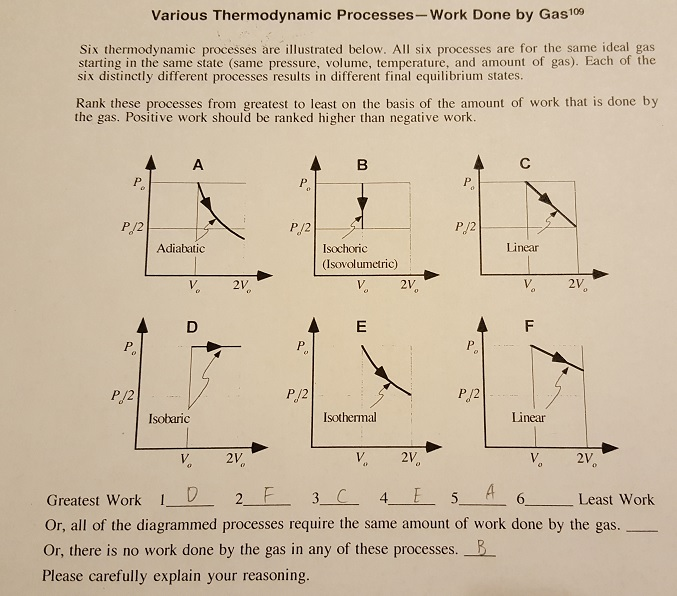
We will explore this idea in greater detail in Section 4.4. V plot will give us the work done on or by the gas. x plot gave us work done, the area under a P (V) vs. The other parts of the path represent a constant volume process. In a special case is when work being done is at constant pressure, work simplifies to: (4.2.7) W P V. If the trip took 8 hr, calculate the average speed of the car in km/hr and m/s. how much work is done by the gas if its pressure changes with volume via (a) path A. If you choose to fix pressure instead of volume, equation (2) changes to. The odometer of a car reads 2000 km at the start of a trip and 2400km at the end of the trip. of several hundred years, but much of the most important work was done in.
How much distance will he cover (a) in one minute and (b) in one second. Amit is moving in his car with a velocity of 45km/hr. Calculate the acceleration of the bicycle in both the cases. Another way to increase the internal energy of a fluid is to do work on it by. The piston moves up a distance y therefore, the work done by the. Then he applies brakes such that the velocity of bicycle comes down to 4m/s in the next 5s. temperature, pressure and internal energy of the fluid will increase. As the gas in the cylinder expands, the force exerted by the gas on the piston is F PA.

Starting from a stationary position, Bhuvan paddles his bicycle to attain a velocity of 6m/s in 30s. (a) What is the total distance to be covered by the athletics? (b) What is the displacement of the athletics when they touch the finish line? (c) Is the motion of the athletics uniform or non-uniform? (d) Is the displacement of an athletic and the distance covered by him at the end of the race equal? 8. The piston moves inward, increasing internal pressure. Suppose the length of the track was 200m. Since Vf > Vi, w < 0 and we say that work is done by the gas. In along distance race, the athletics were expected to take four rounds of the track such that the line of finish was same as the line of start. Find the average speed and average velocity of Vishnu. The magnitude of the work done when a gas expands is therefore equal to the product of the pressure of the gas times the change in the volume of the gas. He covers 180m in one minute by swimming from one end to the other and back along the same straight path. What is the average speed of the object? 6. An object travels 16m in 4s and then another 16m in 2s.
#Workdone with differenet pressure full
Calculate the distance and displacement (i) when it completes half the circle (ii) when it completes one full circle. When crafting your response, think of what strategies you use to stay calm in high-pressure situations. Think of how you handle stress While working under pressure, you need ways to lower your stress levels.

An object is moving in a circle of radius ‘r’. Follow these steps to successfully answer, ‘How do you work under pressure’: 1. Calculate the total distance travelled and the displacement. A body travels a distance of 15m from A to B and then moves a distance of 20m at right angles to AB. Calculate the distance travelled and the displacement. Wn vertically upwards reaches a maximum height ‘h’. Calculate the distance covered and the displacement when it competes 3 revolutions. A particle is moving in a circle of diameter 5m. We correspondingly remove the negative sign on the definition for work done by the system and the enthalpy (flow) work recovers a negative sign.1. In the Clausius/mechanical engineering paradigm, $dU = \delta q - \delta w$. The amount of work done upon an object depends upon the amount of force (F) causing the work, the displacement (d) experienced by the object during the work. $$ w = \int\ V\ dp $$ Alternative Perspective $$ dH \equiv dU + d(pV) = \delta q + V dp $$ Work done in compressing a gas at constant temperature may be expressed as the product of pressure P times the change in volume dV that is, W PdV. $$ w = - n R T \ln(p_f/p_i) $$ Reversible Flow - Enthalpy Work Steady Flow Work $$ W =\int_ = n R T / V$ I've seen work often represented by the formula $$W = PΔV$$īut there are also other formulas, which represent different types of work.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
